Mad Hedge Technology Alerts!
Mad Hedge Technology Letter
April 2, 2018
Fiat Lux
Featured Trade:
(WHY THERE WILL NEVER BE AN ANTITRUST CASE AGAINST AMAZON)
(AMZN), (WMT), (MSFT), (FB), (DBX), (NFLX)
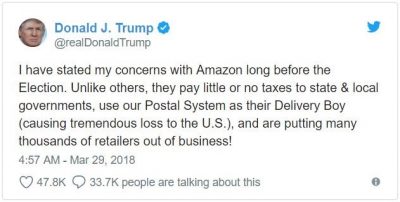
POTUS's Amazon tweet of March 29 has given investors the best entry point into Amazon (AMZN) since the January 2016 sell-off. Since then, the stock has essentially gone up every day.
Entry points have been few and far between as every small pullback has been followed by aggressive buying by big institutional money.
The 200-point nosedive was a function of the White House's dissatisfaction of leaked stories that would find their way into the Washington Post owned by Amazon CEO Jeff Bezos, my former colleague and good friend.
Although there are concerns about Amazon's business model, notably its lack of actual profits, there is no impending regulatory action. And, if there is one company that's in hotter water now, it's Facebook (FB), which inadvertently sells every little detail about your personal life to third-party Eastern European hackers.
Amazon's e-commerce business does not violate the Federal Trade Commission Act of 1914 of "deceptive" or "unfair practices."
The American economy has rapidly evolved thanks to hyper-accelerating technology, and the jobs required to support the modern economy have changed beyond all recognition.
The Clayton Antitrust Act of 1914 addressing harmful mergers that destroy competition hasn't been breached either since Amazon has grown organically.
Analyzing the most comprehensive law, the Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890, which was originally passed to control unions, espouses economic freedom aimed at "preserving free and unfettered competition as the rule of trade."
And, in a way, Amazon could be susceptible, but it would be awfully difficult to persuade the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) Antitrust Division and would take a decade.
Amazon's business model will change many times over by the time any antitrust decision can be delivered, or even entertained.
Helping Amazon's case even more is the DOJ interpretation of the three antitrust rules. It is the company's duty to first and foremost protect the consumer and ensure business is operating efficiently, which keeps prices low and quality high. Antitrust laws are, in effect, consumer protection laws.
Amazon's e-commerce segment epitomizes the DOJ's perception of these 100-year-old laws.
The controversial part of Amazon's business model is funneling profits from its Amazon Web Services (AWS) division as a way to offer the lowest prices in America for its e-commerce products.
This strategy has the same effect as dumping since it is selling products for a loss, but it is not officially dumping.
POTUS has usually delivered more bark than bite. The steel and aluminum tariffs went from no exceptions to exceptions galore in less than a week. Policies and employees change in a blink of an eye in the White House.
The backlash is a case of the White House not being a huge admirer of Amazon, but individual government workers probably have Amazon boxes stacked to the heavens on their doorsteps.
It is true that Amazon has negatively affected retail business. It is doing even more damage to traditional shopping malls, which it turns out are owned by close friends of the president. The mom-and-pop stores have disappeared long ago. But Amazon could argue this trend is occurring with or without Amazon.
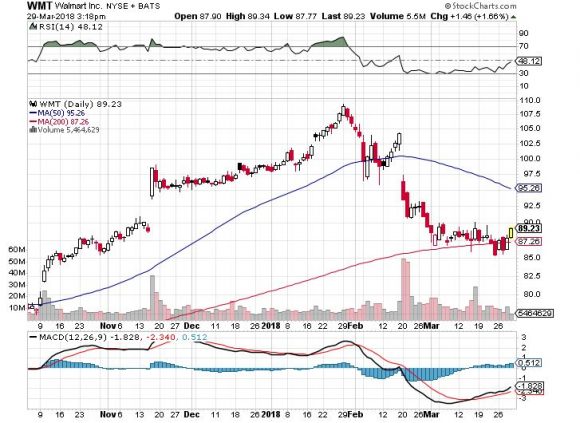
In addition, Walmart (WMT) was the original retail killer, and it currently is morphing into another Amazon by investing aggressively into its e-commerce division. Does the White House go after (WMT) next?
Unlikely.
Amazon didn't create e-commerce.
Amazon also didn't create the Internet.
Amazon also does pay state and local taxes, some $970 million worth last year.
Technology has been a growth play for years.
Investors and venture capitalists are willing to fork over their hard-earned cash for the chance to own the next Google (GOOGL) or Apple (AAPL).
Many investors do lose money searching for the next unicorn. A good portion of these unicorns lose boatloads of money, too.
Spotify, slated to go public soon, is a huge loss-maker and investors will pay up anyway.
Investors went gaga for Dropbox (DBX), already up 40% from its IPO, and it lost $112 million in 2017.
The risk-appetite is hearty for these burgeoning tech companies if they can scale appropriately.
Should investors be prosecuted for gambling on these cash-losing businesses?
Definitely not. Caveat emptor. Buyer beware.
It is true that Amazon pumps an extraordinary percentage of revenues back into product development and enhancement.
But that is exactly what makes Amazon great. It not only is focused on making money but also on making a terrific product.
The bulk of its enhancement is allocated in warehouse and data center expansion. Splurging on more original entertainment content is another segment warranting heavy investment, too, a la Netflix (NFLX). Did you spot Jeff Bezos at the last Oscar ceremony?
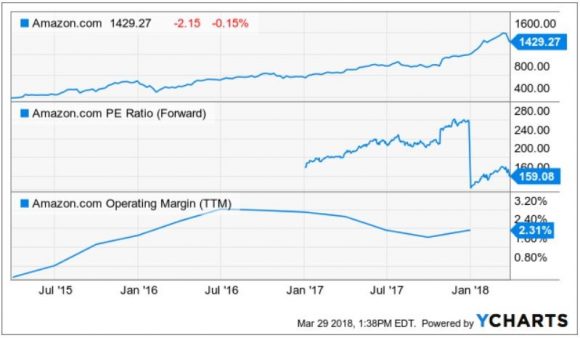
Contrary to popular belief, Amazon is in the black.
It has posted gains for 11 straight quarters and expects a 12th straight profitable quarter for Q1 2018.
The one highly negative aspect is profit margins. It is absolutely slaughtered under the current existing model.
However, investors continually ignore the damage-to-profit margins and have a laser-like focus on the AWS cloud revenue.
Amazon's AWS segment could be a company in itself. Cloud revenue last quarter was $5.11 billion, which handily beat estimates at $4.97 billion.
Amazon's cloud revenue is five times bigger than Dropbox's.
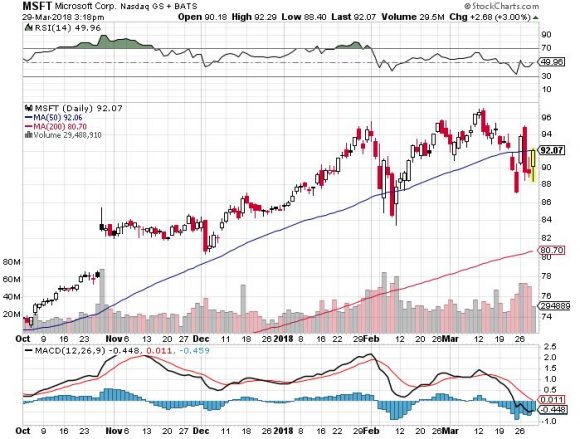
The biggest threat to Amazon is not the administration, but Microsoft (MSFT), which announced amazing cloud revenue numbers up 98% QOQ, and has grown into the second-largest cloud player.
(MSFT) is equipped with its array of mainstay software programs and other hybrid cloud solutions that lure in new enterprise business.
(MSFT) has the chance to break Amazon's stranglehold if it can outmuscle its cloud segment. However, any degradation to Amazon's business model will not kill off AWS, considering Amazon also is heavily investing in its cloud segment, too.
Lost in the tweet frenzy is this behemoth cloud war fighting for storage of data that is somewhat lost in all the political noise.
This is truly the year of the cloud, and dismantling Amazon is only possible by blowing up its AWS segment. The more likely scenario is that AWS and MSFT Azure continue their nonstop growth trajectory for the benefit of shareholders.
Antitrust won't affect Amazon, and after every dip investors should pile into the best two cloud plays - Amazon and Microsoft.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Quote of the Day
Mad Hedge Technology Letter
March 29, 2018
Fiat Lux
Featured Trade:
(TECHNOLOGY'S UPSIDE IN THE TRADE WAR)
(RHT), (DBX), (SPOTIFY)