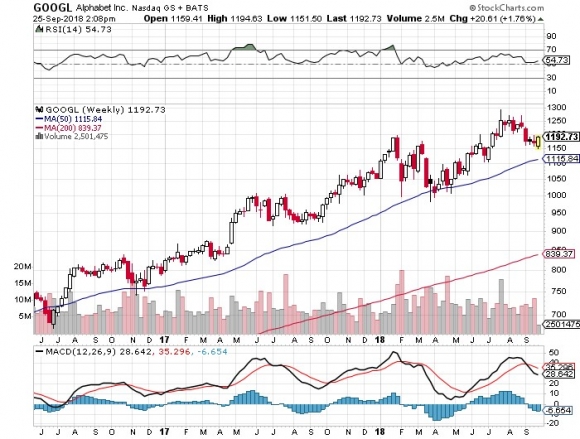
It was the kind of dinner invitation I couldn’t turn down. What I learned was amazing.
I usually prefer to spend my evenings at home catching up on my research, calling customers, and plotting my next great Trade Alert.
So, it takes a lot to get me out of my cozy digs, especially given the recent incredible sunsets we have been getting.
Attending would be senior executives from Tesla (TSLA), General Motors (GM), and engineering professor from the University of California at Berkeley, and the California Air Resources Board.
With US car stocks going ballistic lately, I thought the event would be timely.
The dinner was hosted by a retired billionaire from Microsoft at the top of the Mark Hopkins Hotel in San Francisco.
The topic for discussion would be the very long-term future of the car industry.
I get invited to these things because the guests want to know how their views would fit in within a long-term global geopolitical/economic context, my own particular specialty.
I didn’t want to cramp anyone’s style so I kept my notebook under the table and scribbled away blindly, and illegibly. There’s no particular story line here.
I’ll just give you my random thoughts.
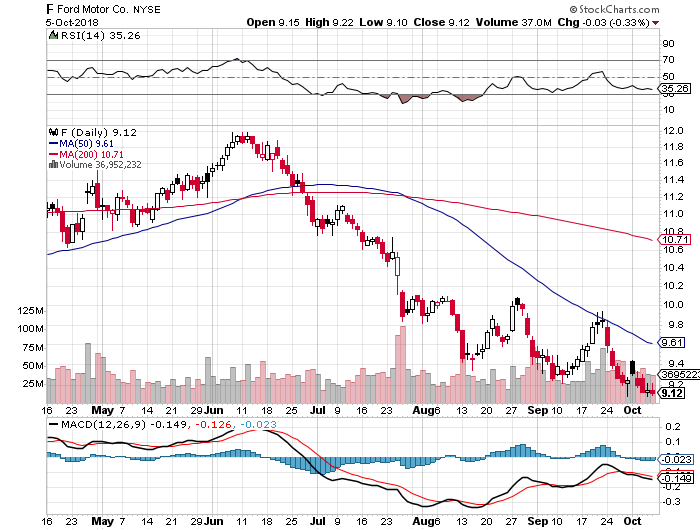
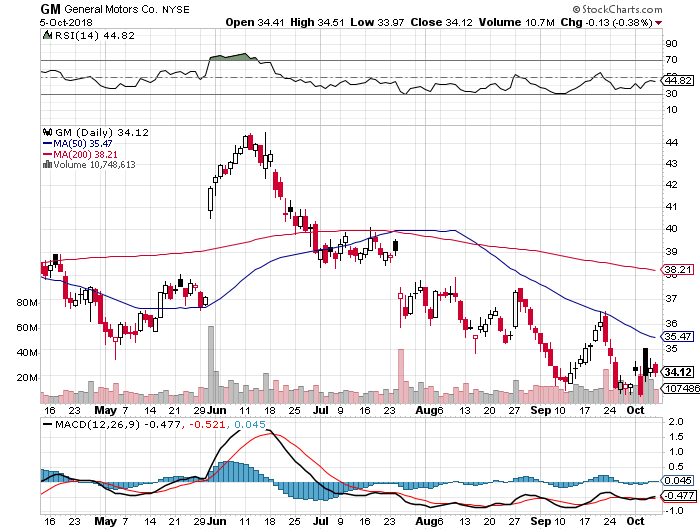
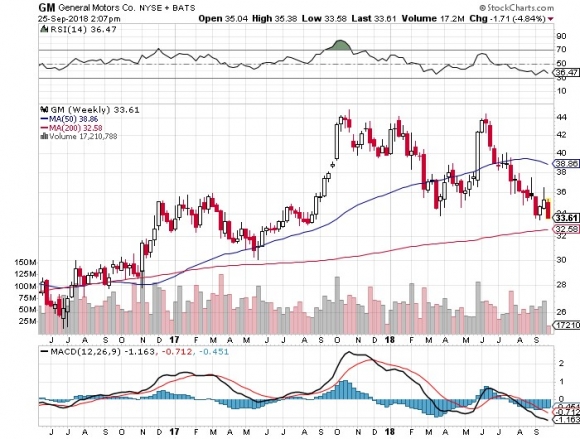
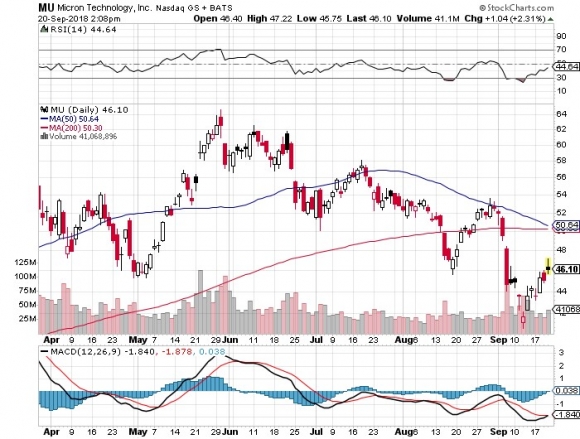
(GM) launched its second-generation Chevy Volt in 2015, and the customer response has been fantastic. The company is building a new $400 million battery plant on the east coast to help meet demand.
Some 60% of the buyers are coming from other automakers. It is fast becoming the new face of Chevy, like the Corvette Stingray and Camaro of years past.
The future is in a 200-mile range $30,000 car, and the Volt is that car, followed by the recently launched all electric Bolt.
Customers want to get away from oil and will only buy the products that accomplish that, be they hybrids or all electric.
He also mentioned that GM is launching an electric bike, which is already widespread in Europe. Not a big needle mover there.
The Tesla guy then proceeded to jump all over him, saying the Volt was “green washing” as usual, since it represents only a tiny fraction of the company’s sales.
GM had a vested interest in promoting the internal combustion engine, in which it had made a century long investment.
Its real focus can be seen in the giant new Suburban factory it was now building in Texas.
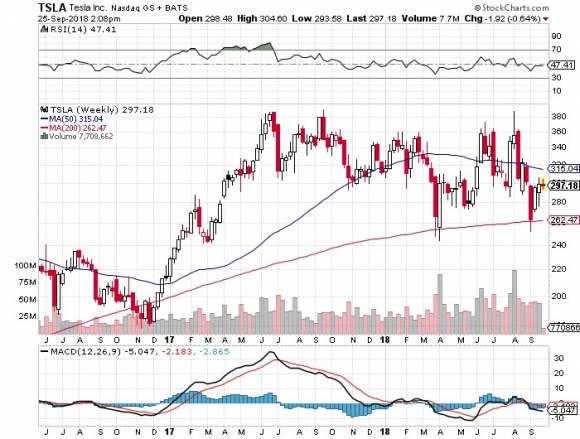
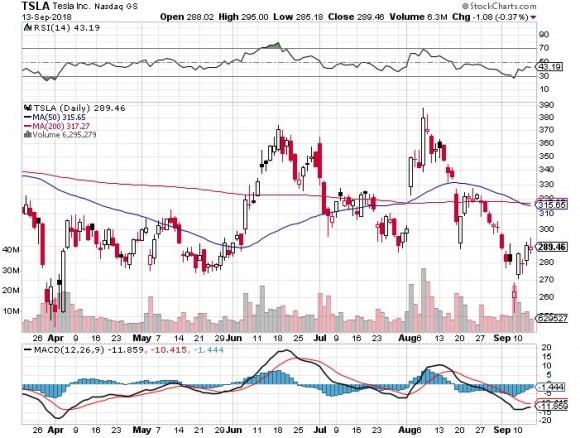
Mr. Tesla had driven from the south Bay with his S-1 entirely on autopilot.
The hardware has already been pre-installed in every S-1 produced since 2014, and all that is needed to make them self-driving is to execute a wireless overnight software upgrade.
What is truly amazing is that each car will have a learning program unique to the vehicle. If it misses a hard turn the first time, it will remember that turn and then make it perfectly every time from then on.
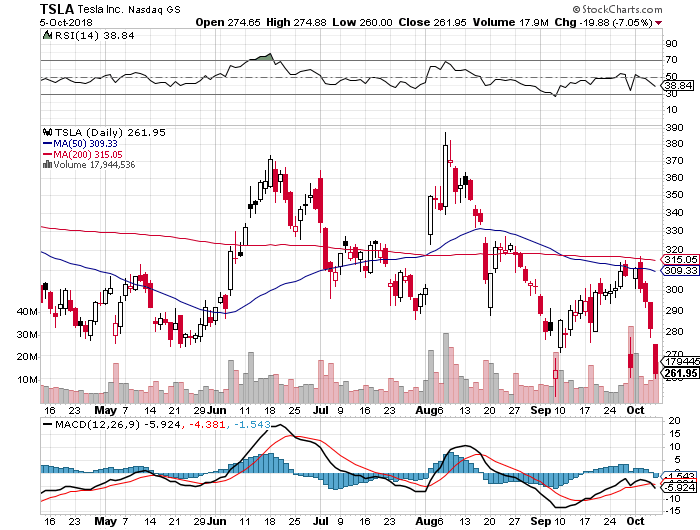
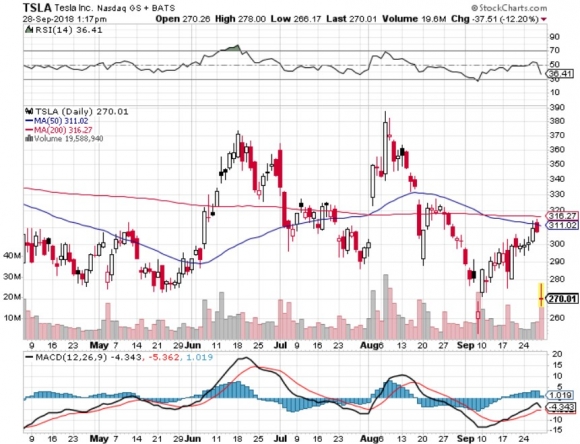
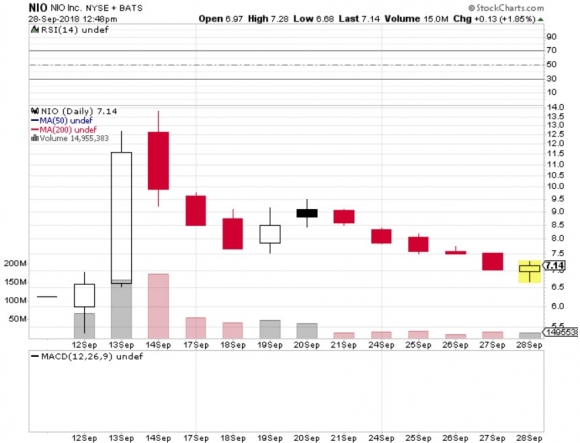
The Tesla person said that with the new Gigafactory the company will be on schedule for a tenfold ramp up in car production by 2020.
The $35,000 Tesla 3 that will make this possible will be offered in two wheel and four wheel drive variations. That will take them from 92,000 units a year to 500,000. Q3 2018 Production has already reached 53,000.
I asked him if this means that if your wife suspects you of cheating, will your Tesla rat you out. He answered, “Only if she is a coder.”
Then I wondered what would stop Tesla from selling your driving habits to marketers who would then make special offers from stores you prefer.
A previous Tesla experiment landed me a pair of Seven for All Mankind designer jeans for half off.
Tesla outsells every other luxury car of its class, including the Mercedes S class, the BMW Series 7, and the Audi 8.
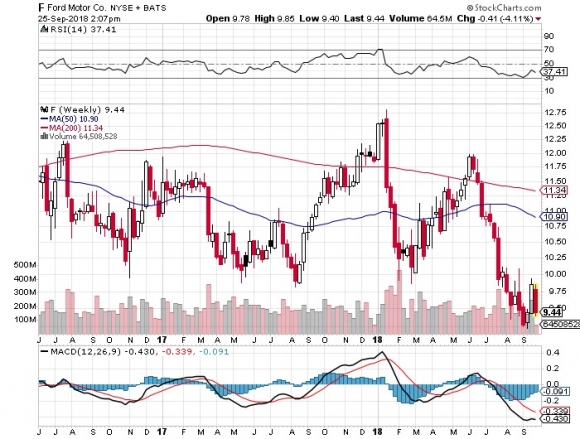
Among the US car industry, only Ford and Tesla have never filed for bankruptcy. Tesla is the first new car manufacturer to succeed since Chrysler made its debut in 1928.
I asked about the S-1 maximum single charge range achieved by a driver.
An enthusiast in Norway managed to take one 800 miles on a flat track with no wind and perfect conditions. Wow! My drive from Lake Tahoe record of 400 miles doesn’t come close, and that involved a 7,000 foot decline from the High Sierra crest.
I also enquired about the Cambridge University battery breakthrough (click here for “Battery Breakthrough Promises Big Dividends.”
He said he was aware of it, but that it takes a long time to get a technology from the bench to the marketplace.
Just with their own in-house tinkering, Tesla is boosting battery ranges by 3-5% a year. The current S-1 gets a 305-mile range, compared to my four-year-old 255-mile range.
The Berkeley professor made some interesting observations about Millennials.
He said that while 75% of baby boomers got drivers licenses at 16, and 70% of Generation Xer’s did so by then, only 55% of Millennials took to the road at that age.
The rule of thumb for anything regarding Millennials is that they do everything late.
The gentleman from the Air Resources Board brought out some interesting facts.
More than 80% of all cancer-causing chemicals entering the atmosphere come from diesel engines, so a major effort will be made to cut back emissions from commercial trucks.
Look for the electric fleet coming to a neighborhood near you. Goodbye Volkswagen!
Workplace charging of employee cars will be the next big growth area for charging stations.
Half of all greenhouse gases derive from the burning of oil. The biggest savings in greenhouse gas emissions will come from a clampdown on the refining industry.
Think Koch Brothers.
I was amazed at his commitment to meet California’s goal of obtaining 50% of its energy from alternative sources by 2030.
The oil industry managed to exempt gasoline from the legislation, SB 350. But Governor Jerry Brown put it back in through an executive order.
The state is paying for the initial build-out of hydrogen refueling stations for the new $57,500 Toyota Mirai. A single tank will take the fuel cell vehicle 312 miles.
The state is making major investments in biofuel, planning to obtain 10% of the 50% target from this source.
During a slow moment, I asked a bleach blond trophy girlfriend sitting next to me of her interest in electric cars, expecting the worst.
To my surprise, she said that last summer, she drove an electric bike from New York to Los Angeles, towing a trailer with a solar panel cut in half to provide power.
The southern route avoided the high mountain ranges. I noticed she seemed unusually tanned, and it wasn’t from a can.
I was humbled. For once, I knew less about electric cars than anyone else in the room.
After the dinner, I went up to the Tesla executive and told him “Job well done.” I used to own one of the oldest S-1’s, number 125 off the assembly line, until it was totaled by a drunk driver on Christmas Eve.
I even tested to their safety claims.
Thank you, Tesla! You saved my life!