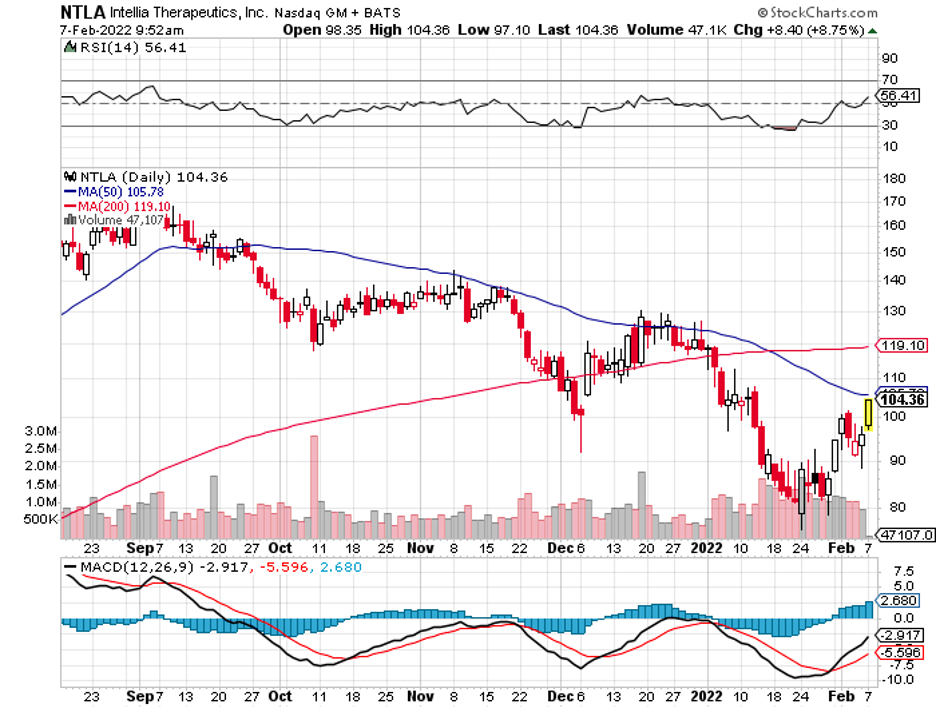
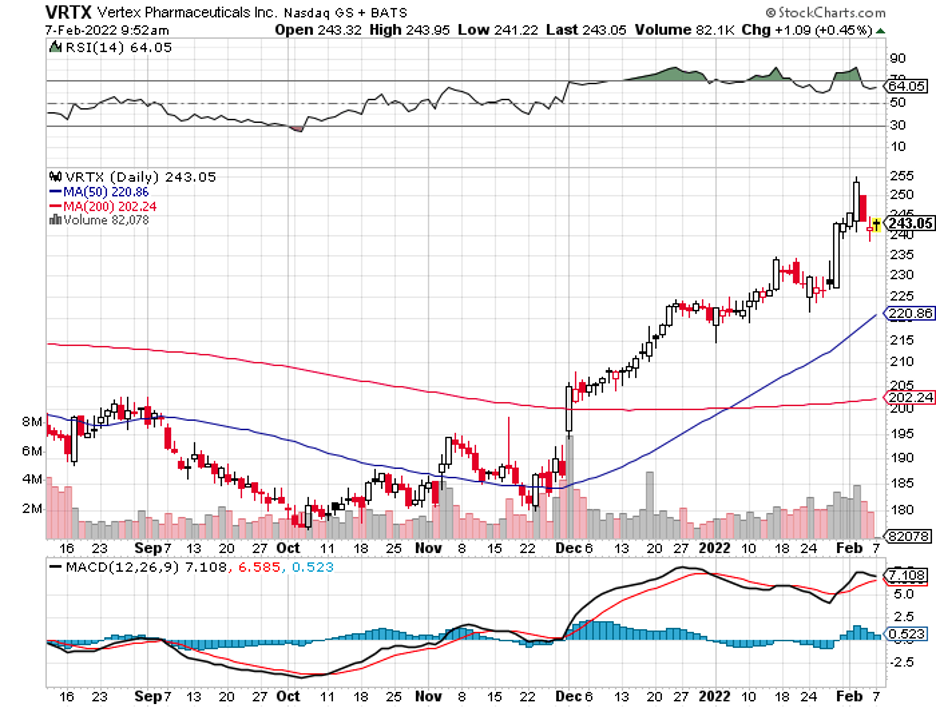
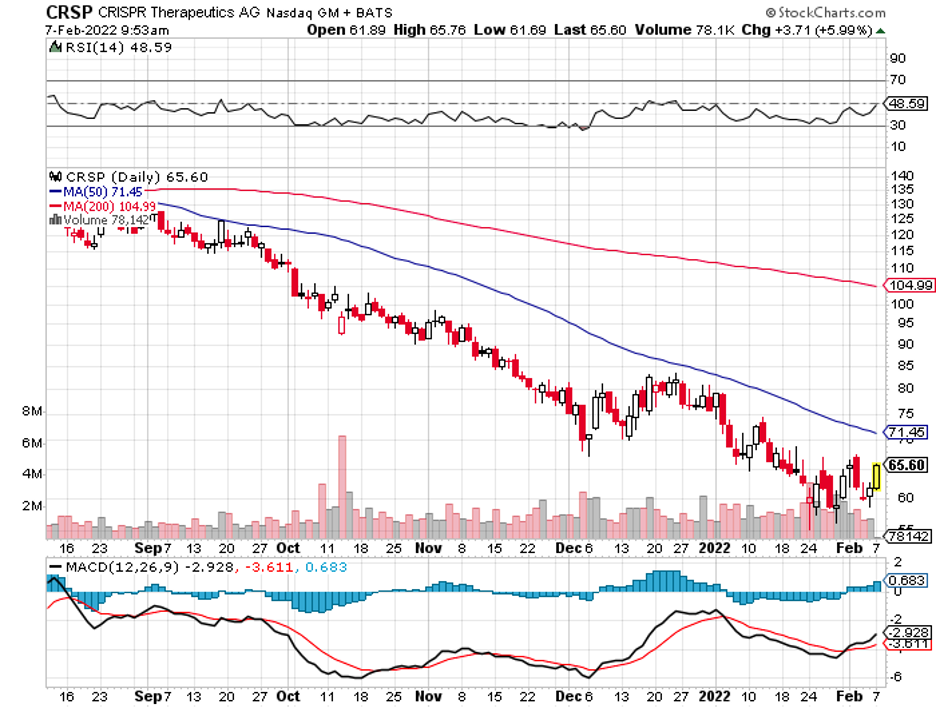
Some stocks bring quick and easy gains, and those are thrilling. However, a key strategy behind a successful portfolio is always including solid players that deliver excellent returns in the long run.
One of the things I appreciate about investing in the healthcare sector is that this industry is primed to perform well no matter what happens to the market.
After all, people will continue to depend on their products and services regardless of the situation in the financial and economic world.
In the biotechnology and healthcare sector, an excellent way to ensure this is to evaluate a company’s pipeline.
This serves as a good indicator of whether the business has the capacity and potential to generate revenue in the years to come. It’s also advisable to check out a company’s general financial picture and, of course, its strategy. Those elements play critical roles in tomorrow’s performance.
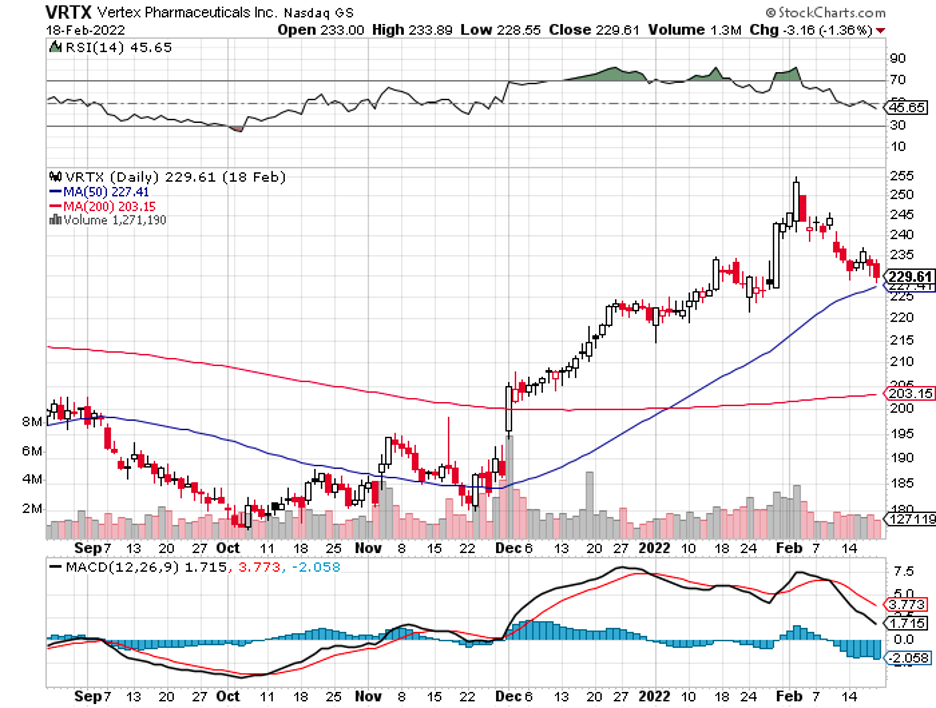
With these criteria in mind, one of the biotechnology names that stand out in the field is Vertex Pharmaceuticals (VRTX).
With a market capitalization of $58.45 billion, Vertex is considered one of the biggest biotechnology companies in the world.
To date, it is included in the Top 5 list of iShares Nasdaq Biotechnology ETF (IBB). Over the years, the company has primarily concentrated on the cystic fibrosis (CF) field.
With its leading CF treatment, Trikafta, gaining approval for a triple combination back in 2019, Vertex has cornered practically 90% of the market.
Unfortunately, Vertex’s share price has remained relatively unchanged for the past two years.
This stagnant performance could be attributed to the disappointing Phase 2 results of its rare liver disease treatment VX-814 in October 2020 and respiratory medication VX-864 in June 2021.
Due to the setbacks from these studies, investors have started to question Vertex’s ability to come up with a marketable treatment outside its CF portfolio.
Vertex posted revenue increases in its recent reports despite these disappointing results.
In the fourth quarter of 2021, the company reported $2.073 billion in revenues, indicating a 27% increase year-over-year, along with an impressive 31% profit growth.
As expected, the revenue boost was courtesy of Trikafta, which recorded a 55% increase in its annual sales.
For the entire 2021 fiscal year, Vertex raked in $7.57 billion in revenues and $3.38 billion in profits, showing off a notable 45% net margin.
Prior to this report, Vertex’s initial guidance for its 2021 revenues was at $6.8 billion.
At that time, experts already believed that the company might be overestimating its capacity, especially considering the setbacks of the trials.
However, it managed to exceed expectations.
Surprisingly, Vertex disclosed an even higher fiscal outlook for 2022 at $8.5 billion. Considering that the company tends to be conservative in its estimates, the following months would definitely bring exciting breakthroughs for Vertex.
In fact, if we look at its track record, there’s a very good chance that the $8.5 billion annual revenue estimate would reach $8.8 billion or even hit $9 billion by the end of 2022.
In terms of its pipeline, Vertex has been working on strengthening its hold in the CF market. This becomes even more necessary with AbbVie (ABBV) hot on its heels with its own version of a triple combination CF therapy expected to rival Trikafta.
Outside its CF program, there are roughly 10 assets queued in various stages of clinical trials.
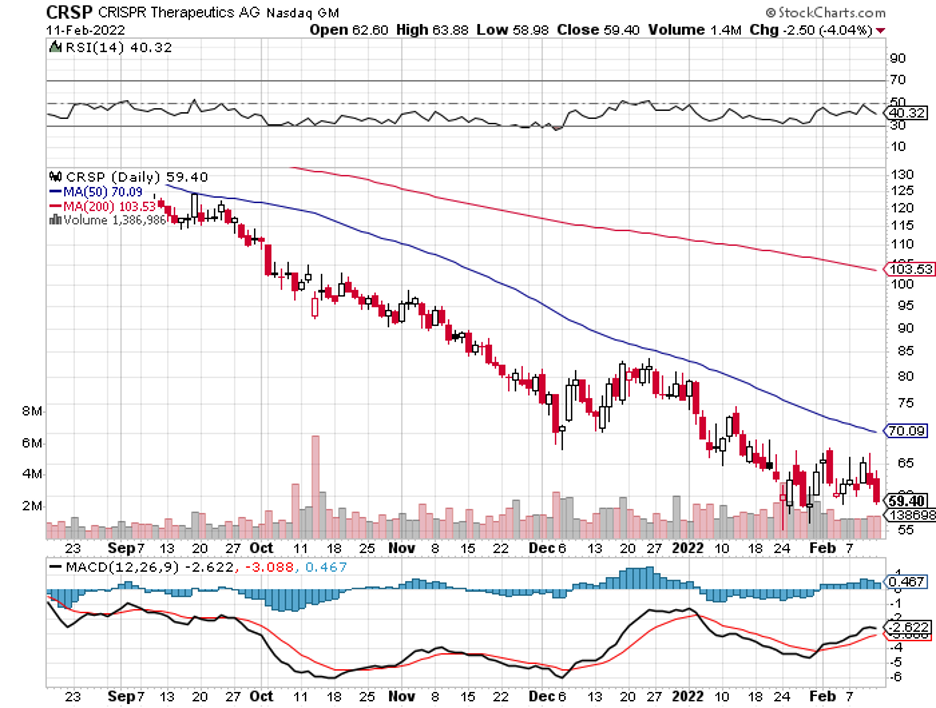
So far, the most advanced is its mRNA-based cell therapy collaboration with CRISPR Therapeutics (CRSP). The treatment, called CTX001, is being developed to target sickle cell disease and beta-thalassemia.
To date, CTX001 is already in Phase 3. It’s slated for regulatory submission to the FDA sometime in the third or fourth quarter of 2022. In terms of profits, CTX001’s peak sales is projected at $1.3 billion.
Another promising candidate is kidney disease treatment VX-147, which is in Phase 2.
Two more candidates are in Phase 2, diabetes cell therapy VX-880 and potential opioid substitute VX-548. While additional trials are still needed, both are anticipated to become blockbuster treatments and game-changers when they enter the market.
Looking at Vertex’s pipeline and the progress of its candidates, it’s safe to say that the company has the capacity to come up with blockbusters outside its CF program.
Moreover, Vertex has an outstanding investment ability due to its high cash balance worth more than $7.5 billion and an impressive balance sheet.
This means that Vertex has the capability to participate in a significant acquisition in the following years in an effort to bolster its pipeline. In this vein, an obvious and alluring candidate would be CRISPR Therapeutics, which is currently valued at $4.49 billion.
Overall, Vertex is a remarkable biotechnology company that has specialized in a lucrative niche for several years, equipping it with the ability to successfully monopolize the sector.
Although market volatility has recently affected it, Vertex still managed to report revenue growth and promising data from its trials. With its relative financial strength and excellent pipeline, I believe this makes the stock a good investment in the long term.